Level 2 EV Home Charger: Electrical Wiring
(North America)
Canada/USA residential voltage is 120-240 volts
Condominium/Commercial/industrial buildings voltage is 120-208 volts
Consult local electrical codes for local requirements
For Condos - it is more cost effective in the long term to deploy EV CMS
(EV Charging Management Software)
Table 1: Level 2 EV-Chargers (EVSE or Electrical Vehicle Service Equipment)
| Circuit Breaker Size | Sample applications | Copper wire size AWG | Charging Current * | Power @ 208 volts | Power @ 240 volts |
| 100 amp | #2 (75°C rating) | 80 amp | 16.6 kW | 19.2 kW | |
| 60 amp | Tesla 3/Y LR, ID4 | #4 | 48 amp | 10 kW | 11.5 kW |
| 50 amp | Campground 50A, Deluxe Elec Range | #6 | 40 amp | 8.3 kW | 9.6 kW |
| 40 amp ** | Std. Electric Range | #8 | 32 amp | 6.6 kW | 7.7 kW |
| 30 amp | Cloth Dryer | #10 | 24 amp | 5 kW | 5.7 kW |
| 20 amp | #12 | 16 amp | 3.3 kW | 3.8 kW |
* Continuous load such as EV charging should/must only draw up to 80% of the circuit breaker's rating to avoid overheating and circuit breaker tripping.
** Most public chargers today are ≈ 6.6 kW.
Sun Country SCH100 (Enphase.com) can deliver 80A (19 kW at 240 volts) and they are typically found at rest areas along highways.
Power ≈ Current x Voltage. For example, 32 A x 208 V ≈ 6656 W, or 6.6 kW
DC chargers have much higher power ratings than Level 2 AC chargers. DC charger power can be 25 kW, 50 kW, 75 kW, 100 kW, 150 kW, 250 kW, 350 kW. Newer EV equipped with 800V battery pack can take full advantage of the high-power chargers (>250kW). Legacy EV battery packs are 400V.
Guestimate rule of thumb: Current generation of DC chargers can deliver 400 A or 500 A at up to 900 volts.
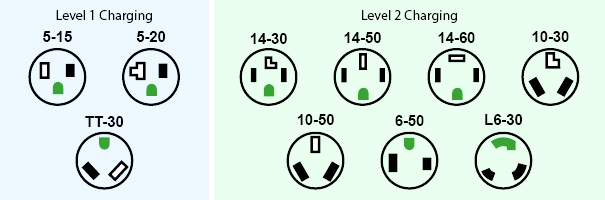
The many electrical plugs used by 240 volts equipment are confusing.
Fortunately EVSV manufacturers and campgrounds have converged on the NEMA type 14-50 plug and receptacle.
Enphase LCS20P comes with NEMA 14-30 plug, which is used by electric cloth dryers.


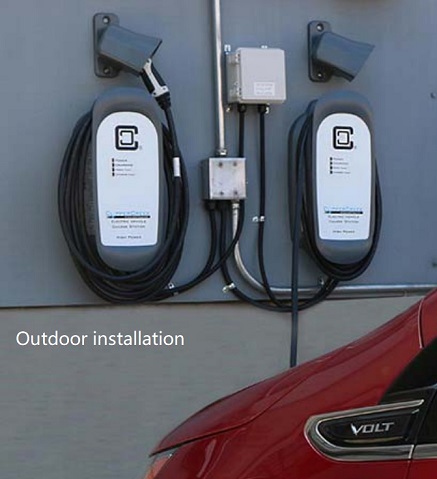
Hardwired EVSE installations. They eliminated the need for plug and receptacle.
Examples of EVSE hardwired installations:


For EV owners doing road trips:
the following apps/websites are useful.
(1) PlugShare: Find the locations of charging stations, what type (DC or level 2) of chargers, plug type, power level, and how many chargers at each location. Sometimes PlugShare can indicate how many of the charging stations are still available for use.
(2) ABRP: For pre-trip planning.
https://abetterrouteplanner.com/
ABRP is especially useful when the highway you plan to use is closed (due to incidents/natural disasters) and you must use a different highway.